- Published on
Docker
- Authors
- Name
- Rammy
Docker Basics
| command | info |
|---|---|
| docker version | |
| docker -v | |
| docker info | |
| docker --help | |
| docker login |
Images
- Each docker image is a layer of stacked mini docker images, such that when an update happens only those required layers will update.
- Docker image is created from docker file.
| command | info |
|---|---|
| docker images | show all images |
| docker run image_name | pull image and create container |
| docker pull image_name | |
| docker images -q | Show image ids |
| docker images -f "dangling=false" | filter images --> show images not associated with any container |
| docker rmi image_name | remove image |
| docker rmi $( docker images -q ) | remove all images not attached to container |
Image --> Containers
- Docker image is like a set of instructions.
- To actually bring the image alive we create containers from that image.
| Command | Info |
|---|---|
| docker ps | show running containers |
| docker ps -a | show all containers |
| docker run --name container_name -it image_name /bin/bash | run container in interactive mode |
| docker start + stop | |
| docker pause + unpause + kill | |
| docker stats container_id/name | provide container memory, io usage |
| docker top container_id/name | display running process of container |
| docker container rm container_id | delete container |
| docker exec -it container_id bin/bash | interact with container by bash |
| docker logs container_id | see docker logs |
| docker container inspect container_id | get all details of the container (port, mount,network etc) |
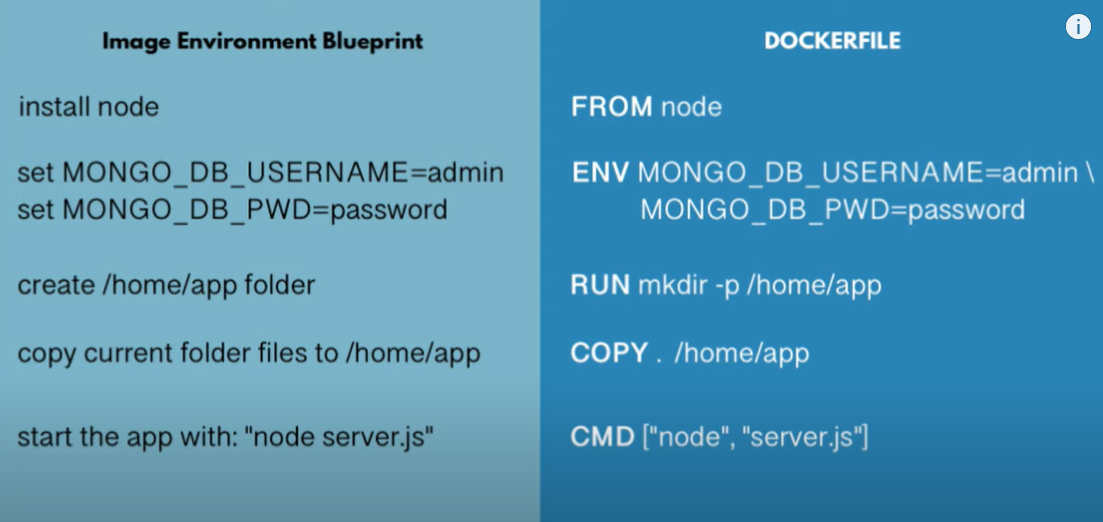
Docker File --> Create Image
- Create Image from Dockerfile :
docker build -t myimageName:tag pathToDockerFile
| Dockerfile Instructions | |
|---|---|
| FROM node | Base image to start from, it could be from scrath as well by using scratch repository from hub |
| MAINTAINER rammy pal kekagmail.com | Maintainer of the dockerfile |
| RUN mkdir -p /home/app | RUN executes with in the container when image is created |
| COPY ./app /home/app | COPY executes on host machine, basically to copy project files to container destination |
| CMD ["node","/home/app/server.js"] | CMD executes when container is created, here when container is started we are running node application |
| - | |
 |
Push Image --> Repository
- In the above step we created our own image from a docker file. Now we can push this local image to a repository.
- The repository could be a private or public repository. Lets use dockerhub repository for simplicity.
| Docker push steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| docker pull hello-world | First lets pull a simple image -> hello-world:latest from docker hub |
| docker tag hello-world:latest docker.io/rammyram/myhello:1.0 | Make sure image is renamed in the following format /repository_address/image_name:tag |
| docker push docker.io/rammyram/myhello:1.0 | Now you can safely push to your repo in docker hub, of course before that you need to do docker login |
| docker pull docker.io/rammyram/myhello | Pulling your repository |
Docker Network
- TODO
Docker Compose
- Docker-compose would be used on the server to deploy all the applications/services.
- The idea is to just provide a single docker compose file to development or testing or deployment team to build the complete project
- Why we need docker compose :
- Consider the case of running mongodb and mongo express client containers on a docker network, the below are the steps needed.
| Steps | Def |
|---|---|
| docker network create | create a network which is shared by both containers |
| docker run -d -p 27017:27017 -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password123 --net myapp --name mongodb mongo | start mongodb database container on network myapp |
| docker run -d -p 8081:8081 -e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME=admin -e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD=password123 -e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER=mongodb --network myapp --name mongo-express mongo-express | start mongo express web client container on network myapp and port mapping on 8081 |
-
What if we have 10 containers or more, we can't keep running these long commands all the time. So we come up with docker compose where we can compose all these commands in a single file.
-
Example :
-
Lets consider the case where our project has 3 services
- database : mongodb
- db client : mongo-express
- shopee_myapp : my nodejs project
-
Step 1 : Create images for all services :
- mongo : ublic image available from docker hub
- mongo-express : public image available from docker hub
- shoppee_myapp: need to create image for our project
- create docker file first
- create image from docker file
- push image to private or public repository
-
Step 2 : Create docker-compose file will all configurations connecting all the 3 services. Check example below -->
-
version: '3'
services:
mongodb:
image: mongo
ports:
- 27017:27017
environment:
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password123
mongo-express:
image: mongo-express
restart: always
ports:
- 8081:8081
environment:
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME=admin
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD=password123
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER=mongodb
depends_on:
- mongodb
shoppee_myapp:
image: docker.io/rammyram/myapp:1.2
ports:
- 3000:3000
environment:
- MONGO_DB_USERNAME=admin
- MONO_DB_PWD=password123
depends_on:
- mongodb
-
Commands :
| commands | info |
|---|---|
| Tool for defining & running multi-container docker applications | |
| use yaml files to configure application services (docker-compose.yml) | |
| docker-compose -f docker-compose.yaml up | start all services in docker-compose with a single command |
| docker-compose -f docker-compose.yaml down | down all services -> down containers + remove containers |
| docker-compose config | check any errors in compose yaml file |
| docker-compose -d | up in detached mode |
| docker-compose up --scale mongodb=4 | scaling a services |
Volumes
- Decoupling container from storage
- Share volume (storage/data) among different containers
- Attach volume to container
- On deleting container data still persists in volumes.
-
Types of volumes :
| Command | Type of volume |
|---|---|
| docker run -v /home/mount/data:/var/lib/mysql/data | Host volumes -> you decide where on the host the reference is made to save data |
| docker run -v /var/lib/mysql/data | Anonymous volumes -> docker takes care of automatically mounting to a location on host ( ex: /var/lib/docker/randon-hash/data) |
| docker run -v app_vol:/var/lib/mysql/data | Named Volumes --> we can create a specific docker volume and set to use that volume. These named volumes are located on host ( ex: /var/lib/docker/volumes/app_vol/data)...suitable for production and also simpler when volume needs to be shared among containers |
Stats
| Command | Stats |
|---|---|
| docker stats | Details on running containers, memory usage |
| docker system df | Disk usage of docker, all images, containers, local volumes, size |
| docker system prune | - Delete stopped containers - Release any unused network & memory |
Status: #done
Tags: #docker_basics #docker_image #docker_container #docker_image #docker_compose
References:
Related: